一、springboot原理探究
1、springboot默认错误处理机制
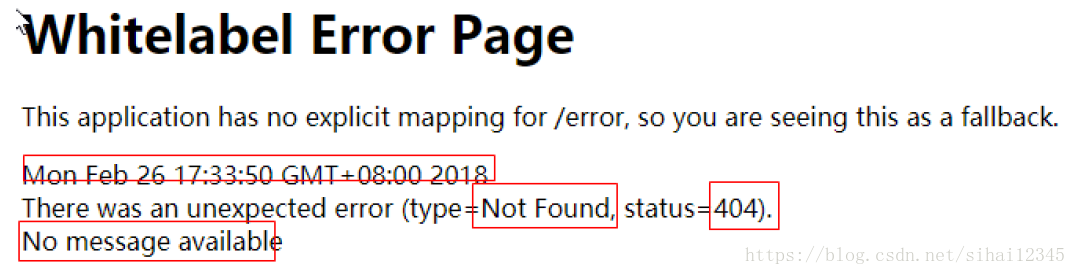
1.1、错误页面
如果没有进行处理出现错误,默认这样处理页面。
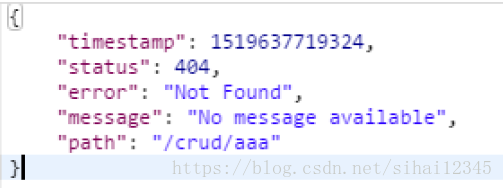
1.2、其他客户端,默认响应一个json数据
2、深入原理
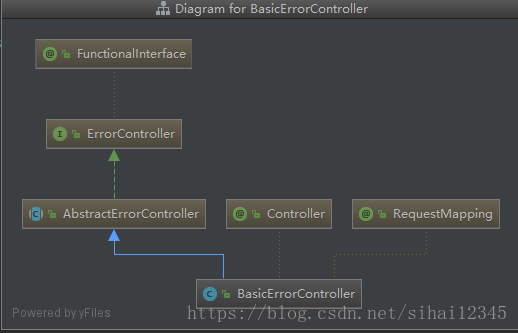
2.1、查看BasicErrorController
这个类是默认处理
/error请求的。下面看看源代码
其中有这样一段代码来处理错误请求:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")//产生html类型的数据;浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面;包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
}
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody //产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理;
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>>(body, status);
}
其类图如下:
下面我们还要看下一个关键类
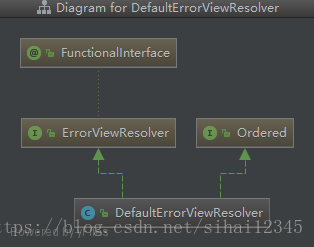
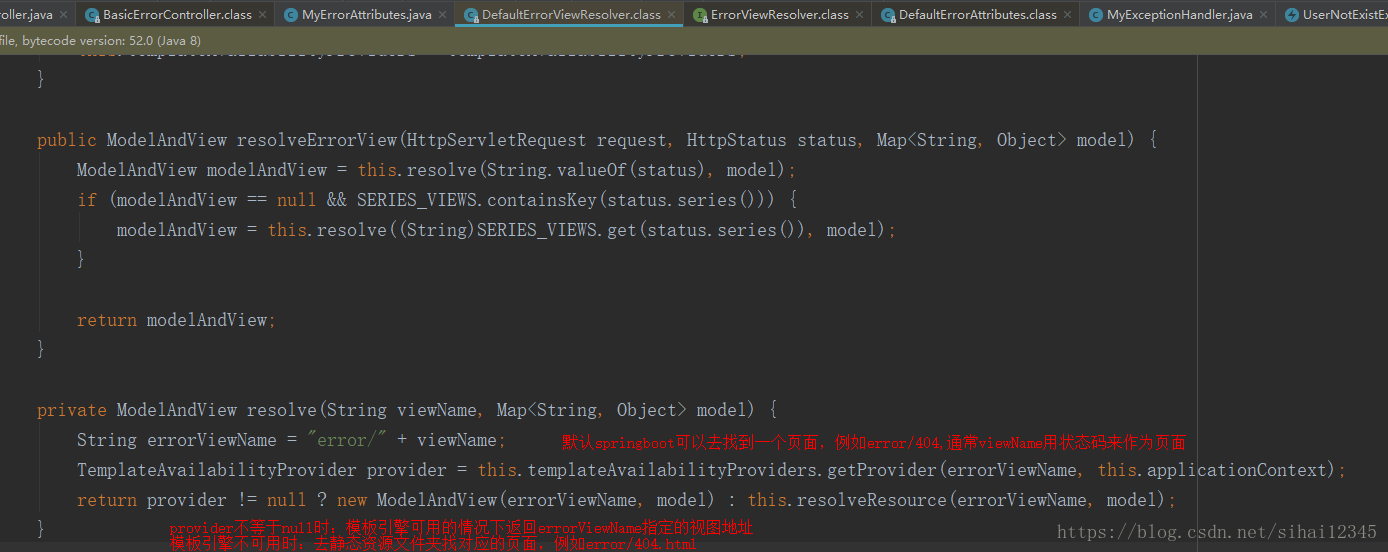
2.2、DefaultErrorViewResolver
先看一下类图
我们看看其中关键代码,就知道springboot如何处理异常:
处理步骤:
一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误;
ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到/
error请求;就会被
BasicErrorController(2.1中讲解的)处理。
二、自定义异常处理响应
2.1、自定义执行流程
1)有模板引擎的情况下;error/状态码
将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的error文件夹下,发生此状态码的错误就会来到 对应的页面。
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误
页面能获取的信息:
timestamp:时间戳
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
例如:
2)没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找(也就是static文件夹)
3)以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面
2.2 单个异常处理
/**
* @author 欧阳思海
* @date 2018/7/25 9:57
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/one")
public class ExceptionControllerTest_2 {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void testException(){
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<String,Object> exceptionHandler(Exception e) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","notexist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
说明:
- 在controller中加入被@ExceptionHandler修饰的类即可(在该注解中指定该方法需要处理的那些异常类)
- 该异常处理方法只在当前的controller中起作用
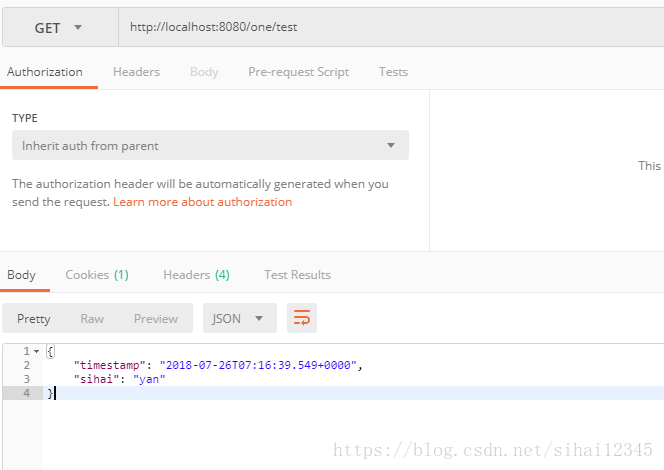
postman输入或者浏览器:http://localhost:8080/one/test
2.3、全局自定义异常处理
2.3.1、自定义异常处理
我们需要写一个MyExceptionHandler类,用
@ControllerAdvice标注和
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)标记具体使用哪个类
/**
* @author 欧阳思海
* @date 2018/7/26 10:58
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","notexist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
说明:
@ControllerAdvice是controller的一个辅助类,最常用的就是作为全局异常处理的切面类
@ControllerAdvice可以指定扫描范围
@ControllerAdvice约定了几种可行的返回值,如果是直接返回model类的话,需要使用@ResponseBody进行json转换
- 返回String,表示跳到某个view - 返回modelAndView - 返回model + @ResponseBody
2.3.2、controller测试
@RequestMapping(value = "/test2", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void testException(){
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
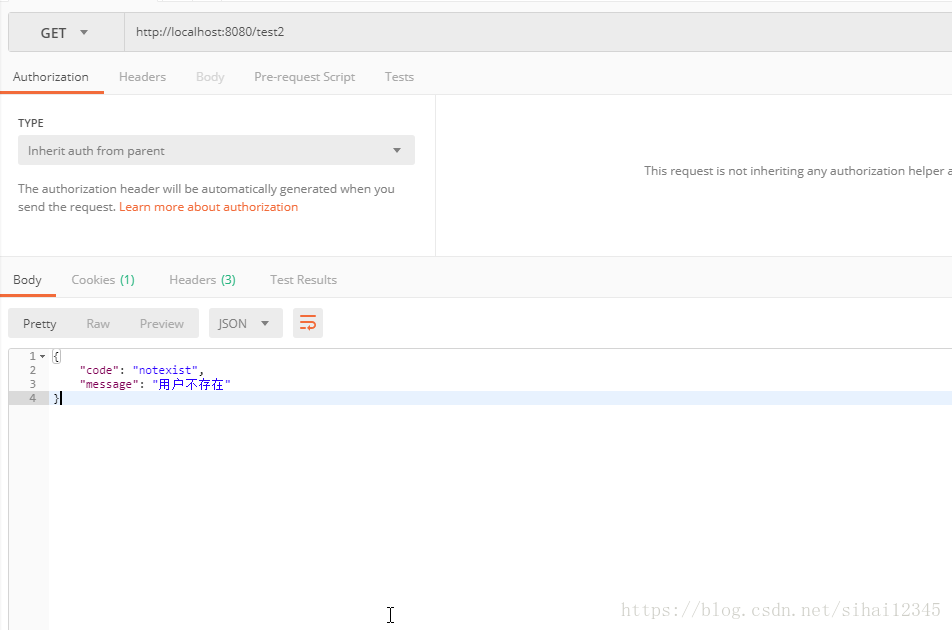
2.3.3、测试结果
在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/test2