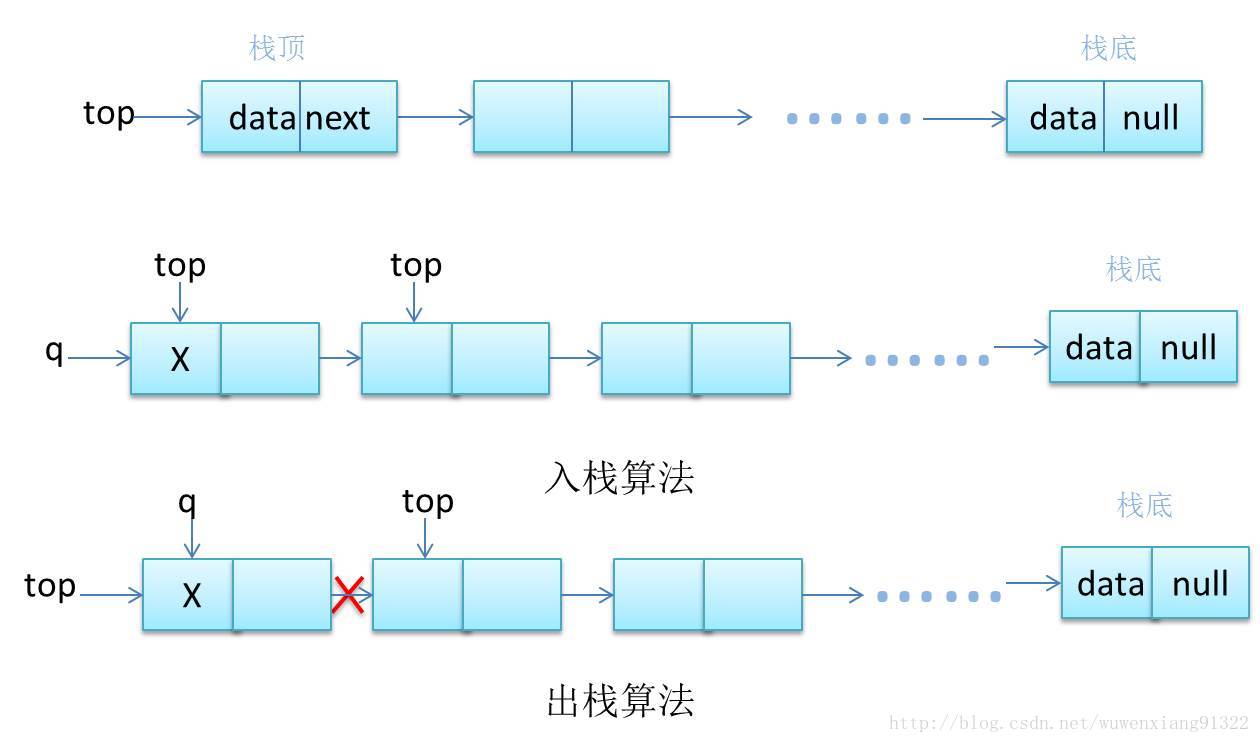
一、堆栈的基本概念:
堆栈(也简称作栈)是一种特殊的线性表,堆栈的数据元素以及数据元素间的逻辑关系和线性表完全相同,其差别是线性表允许在任意位置进行插入和删除操作,而堆栈只允许在固定一端进行插入和删除操作。
先进后出:堆栈中允许进行插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。堆栈的插入和删除操作通常称为进栈或入栈,堆栈的删除操作通常称为出栈或退栈。
备注:栈本身就是一个线性表,所以我们之前讨论过线性表的顺序存储和链式存储,对于栈来说,同样适用。
二、堆栈的抽象数据类型:
数据集合:
堆栈的数据集合可以表示为a0,a1,…,an-1,每个数据元素的数据类型可以是任意的类类型。
操作集合:
(1)入栈push(obj):把数据元素obj插入堆栈。
(2)出栈pop():出栈, 删除的数据元素由函数返回。
(3)取栈顶数据元素getTop():取堆栈当前栈顶的数据元素并由函数返回。
(4)非空否notEmpty():若堆栈非空则函数返回true,否则函数返回false。
三、顺序栈:
顺序存储结构的堆栈称作顺序堆栈。其存储结构示意图如下图所示:
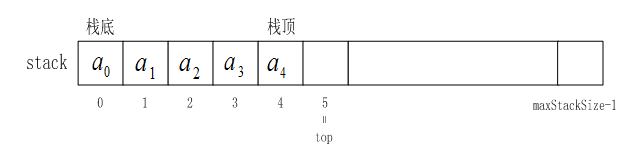
1、顺序栈的实现:
(1)设计Stack接口
(2)实现SequenceStack类
注:栈是线性表的特例,线性表本身就是用数组来实现的。于是,顺序栈也是用数组实现的。
代码实现:
(1)Stack.java:(Stack接口)
1 public interface Stack {<!-- -->
2
3 //入栈
4 public void push(Object obj) throws Exception;
5
6 //出栈
7 public Object pop() throws Exception;
8
9 //获取栈顶元素
10 public Object getTop() throws Exception;
11
12 //判断栈是否为空
13 public boolean isEmpty();
14 }
(2)SequenceStack.java
1 //顺序栈
2 public class SequenceStack implements Stack {<!-- -->
3
4 Object[] stack; //对象数组(栈用数组来实现)
5 final int defaultSize = 10; //默认最大长度
6 int top; //栈顶位置(的一个下标):其实可以理解成栈的实际长度
7 int maxSize; //最大长度
8
9 //如果用无参构造的话,就设置默认长度
10 public SequenceStack() {
11 init(defaultSize);
12 }
13
14 //如果使用带参构造的话,就调用指定的最大长度
15 public SequenceStack(int size) {
16 init(size);
17 }
18
19 public void init(int size) {
20 this.maxSize = size;
21 top = 0;
22 stack = new Object[size];
23 }
24
25 //获取栈顶元素
26 @Override
27 public Object getTop() throws Exception {
28 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
29 if (isEmpty()) {
30 throw new Exception("堆栈为空!");
31 }
32
33 return stack[top - 1];
34 }
35
36 //判断栈是否为空
37 @Override
38 public boolean isEmpty() {
39 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
40 return top == 0;
41 }
42
43 //出栈操作
44 @Override
45 public Object pop() throws Exception {
46 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
47 if (isEmpty()) {
48 throw new Exception("堆栈为空!");
49 }
50 top--;
51
52 return stack[top];
53 }
54
55 //入栈操作
56 @Override
57 public void push(Object obj) throws Exception {
58 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
59 //首先判断栈是否已满
60 if (top == maxSize) {
61 throw new Exception("堆栈已满!");
62 }
63 stack[top] = obj;
64 top++;
65 }
66 }
2、测试类:
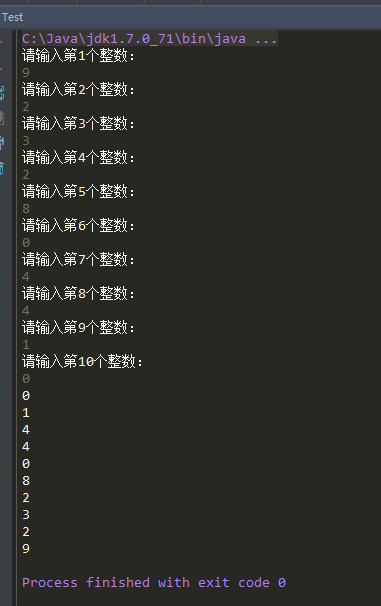
设计一个顺序栈,从键盘输入十个整数压进栈,然后再弹出栈,并打印出栈序列。
代码实现:
(3)Test.java
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Test {
4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
5 SequenceStack stack = new SequenceStack(10);
6
7 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
8 int temp;
9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
10 System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个整数:");
11 temp = in.nextInt();
12 stack.push(temp);
13 }
14
15 //遍历输出
16 while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
17 System.out.println(stack.pop());
18 }
19 }
20 }
运行效果:
四、栈应用
1、括号匹配问题
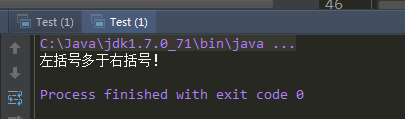
假设算术表达式中包含圆括号,方括号,和花括号三种类型。使用栈数据结构编写一个算法判断表达式中括号是否正确匹配,并设计一个主函数测试。
比如:
{a+[b+(ca)/(d-e)]} 正确 ([a+b)-(ce)]+{a+b} 错误,中括号的次序不对
括号匹配有四种情况:
1.左右括号匹配次序不正确
2.右括号多于左括号
3.左括号多于右括号
4.匹配正确
下面我们就通过代码把这四种情况列举出来。
代码实现
1 public class Test {
2
3 //方法:将字符串转化为字符串数组
4 public static String[] expToStringArray(String exp) {
5 int n = exp.length();
6 String[] arr = new String[n];
7 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
8 arr[i] = exp.substring(i, i + 1);
9 }
10 return arr;
11 }
12
13 //方法:括号匹配问题的检测
14 public static void signCheck(String exp) throws Exception {
15 SequenceStack stack = new SequenceStack();
16 String[] arr = Test.expToStringArray(exp);
17 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
18 if (arr[i].equals("(") || arr[i].equals("[") || arr[i].equals("{")) { //当碰到都是左边的括号的时候,统统压进栈
19 stack.push(arr[i]);
20 } else if (arr[i].equals(")") && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.getTop().equals("(")) { //当碰到了右小括号时,如果匹配正确,就将左小括号出栈
21 stack.pop();
22 } else if (arr[i].equals(")") && !stack.isEmpty() && !stack.getTop().equals("(")) {
23 System.out.println("左右括号匹配次序不正确!");
24 return;
25 } else if (arr[i].equals("]") && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.getTop().equals("[")) {
26 stack.pop();
27 } else if (arr[i].equals("]") && !stack.isEmpty() && !stack.getTop().equals("[")) {
28 System.out.println("左右括号匹配次序不正确!");
29 return;
30 } else if (arr[i].equals("}") && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.getTop().equals("{")) {
31 stack.pop();
32 } else if (arr[i].equals("}") && !stack.isEmpty() && !stack.getTop().equals("{")) {
33 System.out.println("左右括号匹配次序不正确!");
34 return;
35 } else if (arr[i].equals(")") || arr[i].equals("]") || arr[i].equals("}") && stack.isEmpty()) {
36 System.out.println("右括号多于左括号!");
37 return;
38 }
39 }
40 if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
41 System.out.println("左括号多于右括号!");
42 } else {
43 System.out.println("括号匹配正确!");
44 }
45 }
46
47
48 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
49
50 String str = "([(a+b)-(c*e)]+{a+b}";
51 //括号匹配的检测
52 Test.signCheck(str);
53 }
54 }
运行效果:
四、链式堆栈:
栈的链式存储结构称为链栈。
在算法中要用到多个栈时,最好用链表作为栈的存储结构,即用指针来实现栈。用这种方式实现的栈也称为链栈。由于栈的插人和删除操作只在表头进行,因此用指针实现栈时没有必要像单链表那样设置一个表头单元。
1、链栈结构及数据类型
栈的链式存贮结构,也称为链栈,它是一种限制运算的链表,即规定链表中的插入和删除运算只能在链表开头进行。链栈结构见图。
2、代码实现
链表结点LinearNode.java
public class LinearNode<T> {
private LinearNode<T> next;
private T elem;
public LinearNode(){
next=null;
elem=null;
}
public LinearNode(T ele){
next=null;
this.elem=ele;
}
public LinearNode<T> getNext(){
return next;
}
public void setNext(LinearNode<T> node) {
this.next = node;
}
public T getElem() {
return elem;
}
public void setElem(T elem) {
this.elem = elem;
}
}
链表结点LinkedStack.java
public class LinkedStack<T> implements StackADT<T> {
private int count;
// 指向栈顶的指针
private LinearNode<T> top;
public LinkedStack() {
count = 0;
top = null;
}
/**
* 创建一个新的结点,该结点含有一个引用,指向要放置到战中的对象 把新结点的next设置为top 把top引用设置指向当前新结点 递增栈的元素计数
*/
@Override
public void push(T elem) {
// /结点的创建 和 引用声明
LinearNode<T> temp = new LinearNode<T>(elem);
temp.setNext(top);
top = temp;
count++;
}
@Override
public T pop() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("LinkedStack");
}
T result = top.getElem();
top = top.getNext();
count--;
return result;
}
@Override
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("LinkedStack");
}
T result = top.getElem();
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (count == 0);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return count;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
result.append("");
LinearNode<T> temp = top;
while(temp!=null){
result.append(temp.getElem()+"\n");
temp = temp.getNext();
}
return result.toString();
}
}
辅助类实现
EmptyCollectionException.java
public class EmptyCollectionException extends RuntimeException {<!-- -->
public EmptyCollectionException(String collection) {
super("the " + collection + "is Empty!");
}
}
二、链栈应用
1、表达式计算
比如:
3+(6-4/2)*5=23
其后缀表达式为:3642/-5*+# (#符号为结束符)
现在要做的是:
使用链式堆栈,设计一个算法计算表达式,当我们输入后缀表达式后,能输出运行结果。
代码实现:
1 public class Test {
2
3 //方法:使用链式堆栈,设计一个算法计算表达式
4 public static void expCaculate(LinkStack stack) throws Exception {
5 char ch; //扫描每次输入的字符。
6 int x1, x2, b = 0; //x1,x2:两个操作数 ,b字符的ASCII码
7 System.out.println("输入后缀表达式并以#符号结束:");
8 while ((ch = (char) (b = System.in.read())) != '#') {
9 //如果是数字,说明是操作数则压入堆栈
10 if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
11 stack.push(new Integer(Character.toString(ch)));
12 }
13 //如果不是数字,说明是运算符
14 else {
15 x2 = ((Integer) stack.pop()).intValue();
16 x1 = ((Integer) stack.pop()).intValue();
17 switch (ch) {
18 case '+':
19 x1 += x2;
20 break;
21 case '-':
22 x1 -= x2;
23 break;
24 case '*':
25 x1 *= x2;
26 break;
27 case '/':
28 if (x2 == 0) {
29 throw new Exception("分母不能为零!");
30 } else {
31 x1 /= x2;
32 }
33 break;
34 }
35 stack.push(new Integer(x1));
36 }
37 }
38 System.out.println("后缀表达式计算结果是:" + stack.getTop());
39 }
40
41 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
42 LinkStack stack = new LinkStack();
43 //(2+3)*(3-1)/2=5的后缀表达式为:23+31-*2/
44 //方法:键盘输入后缀表达式,输出的得到计算结果
45 Test.expCaculate(stack);
46
47 }
48 }
运行效果: